Hiatal Hernia
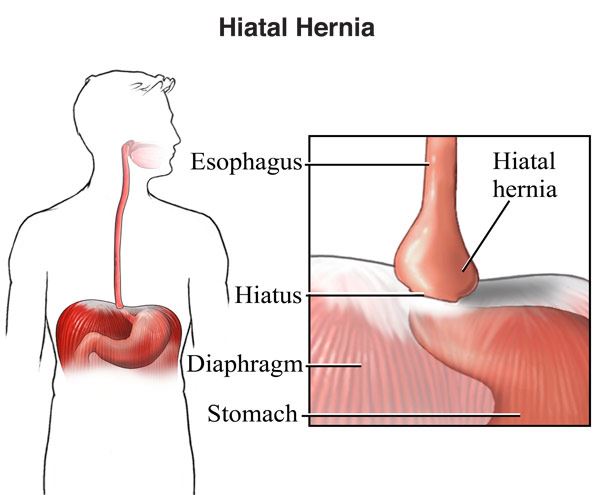
A hernia occurs when an organ pushes through an opening in the muscle or tissue that holds it in place. In this case, a hiatal hernia is a condition where the top portion of the stomach pokes through a small hole in the diaphragm. The diaphragm is the muscle that separates the chest from the stomach, and it contains a small opening in the center called the hiatus.
As long as the hernia isn’t causing any problems, there may not be any reason to have it treated. However, patients who do experience symptoms will have a greater risk for more severe complications and should receive care promptly.
Medical Illustration Copyright © 2019 Nucleus Medical Media, All rights reserved.
Types of Hiatal Hernias
There are two primary types of hiatal hernias:
- Sliding Hernias: This is the most common type of hiatal hernia. In this type, the stomach and lower esophagus slide into the chest through the hiatus. This type does not always require treatment.
- Paraesophageal Hernias: These types of hernias are rarer and more dangerous. In this type, the top of the stomach squeezes through the hiatus and sits next to the esophagus. This can cut off blood supply and cause serious complications.
Causes of Hiatal Hernias
Hernias are caused by a combination of muscle weakness and strains. However, other conditions, traits or habits may also play a role in raising your risk. These conditions are known as risk factors and include:
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: These factors are irreversible and cannot be changed. The more of these risk factors you have, the greater your chance of developing this disease.
- Older age
- Family history/Genetics
- Pregnancy
- Autoimmune Disease: A condition in which your immune system mistakenly attacks your body (e.g. lupus, rheumatoid arthritis and scleroderma).
- Certain congenital abnormalities (i.e. heart defects, neural tube defects, Down syndrome, among others).
Modifiable Risk Factors: These factors can be modified, treated or controlled through medications or lifestyle changes.
- Extreme physical exertion.
- Obesity or having a body mass index “BMI” of 30 or greater.
- Long history of cigarette smoking and/or drug abuse.
Other conditions that contribute to developing hiatal hernias:
- Damage from an injury or surgery.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD)
- Fluid in the abdomen
- Chronic constipation
- Cystic fibrosis
Symptoms of Hiatal Hernias
Some common symptoms of hiatal hernias include:
- Heartburn
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chest pain and/or abdominal pain
- Shortness of breath
- Acid reflux
- Regurgitation (bringing food or liquid back up to the mouth)
However, if you experience any of the following symptoms, you should seek medical treatment immediately:
- Unusual severe pain in the chest or stomach.
- Difficulty passing gas or excrement.
- Vomiting
- Small, black stools
Diagnosis of Hiatal Hernias
Hiatal hernias usually can’t be diagnosed with a physical examination, so your provider will have to arrange tests. These could include one or more of the following:
Treatment of Hiatal Hernias
If you only experience mild symptoms caused by the hernia, then your provider will likely only recommend medication and lifestyle changes. Some treatment options include:
Lifestyle Changes
- Eat a heart-healthy diet.
- Avoid smoking.
- If you are overweight, talk to your doctor about weight loss options.
- Make and keep appointments to see your doctor for routine check-ups and follow-up tests.
- Exercise under the directions of your doctor.
Medications
- Antacids will help neutralize stomach acid.
- Proton pump inhibitors will help block acid production and heal the esophagus.
